Piapplications Cloud Hub
Simplifying connection, integration, automation and AI
The modern business software environment typically is made up of a raft of specialised Accounting, CRM, WMS applications as well as bespoke software solutions. This new breed of applications are nearly all cloud based. To get best value and productivity from the separate cloud applications we need to connect the cloud apps to each other, so that they can interact meaningfully. Connecting cloud apps is what Piapplications’ Cloud Hub does. It’s a programming framework that allows us to build smart connections between cloud applications that can also provide software hosting, secure login and data storage. Hub can also provide an ideal location to implement AI augmentation.
Connectivity:
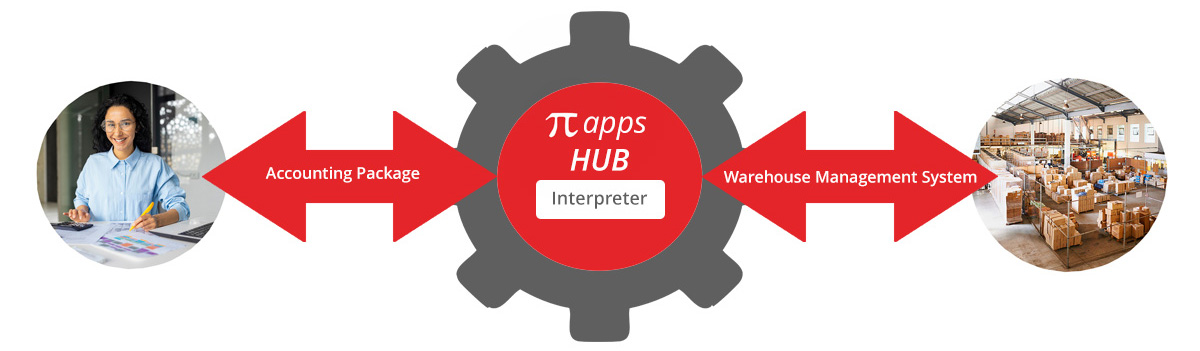
The Piapplications’ Cloud Hub model is primarily about connectivity. In the simplest version of Cloud Hub, you have two third party applications that you want to connect so they can interact with each other.
Each application has its own connection software (called an API). Both external applications can connect to the hub. To do this they need software added that acts as an interpreter so they can communicate meaningfully. The Hub provides the interpreter service.
This simplest hub configuration allows two external applications to connect to each other and communicate effectively via interpreter code.
Most Cloud Hubs, however, provide more than just simple connectivity. It’s easiest to understand starting with a simple model. Then we can progressively add elements.
To start with we have a simple hub with two applications. Let's say a Warehouse Management Platform and an Accounting Platform. A simple hub with application to application connection, allows output from the Warehouse Management System to trigger the generation of an invoice by the Accounting Platform.
Stage two is to be able to manage the process in between the warehouse management software and the accounting package, at least part of the time. To do this we add to the Hub a piece of software that manages that interaction. An example of the interaction might be an admin intervention to allow the addition of a rebate or discount to the invoice after the order has been despatched.
Of course we can add more connections for additional applications (either external or internal) to join the hub. By expanding the simple warehouse and accounting system above you can see how a hub can work with many connected applications.
To our existing warehouse management software and accounting package model, we now want to add order entry. The source of the order could be a full featured ecommerce platform (built into the hub or via API) or something as simple as an excel file upload. The order entry process can then be managed between the acceptance of the order and the placement of the pick / pack / despatch instruction to the warehouse. An example could be addition of bonus “no charge” promotional stock to the order. The bonus stock needs to be picked /packed / despatched but identified as “no charge” in the invoice instruction. The direction for the additional stock needs to come from an admin role, not from the customer. This is achieved by adding an order management dashboard to the hub that allows instructions relating to the bonus stock to be added before the order is sent to the warehouse.
In our simple system the warehouse then provides information back to the Hub that says a consignment note has been raised. This will ultimately trigger an invoice. This may be largely automated. But we want to be able to give a customer specific discount or rebate before the information is passed to the accounting platform. To do this we need to add an Invoice management dashboard to the hub.
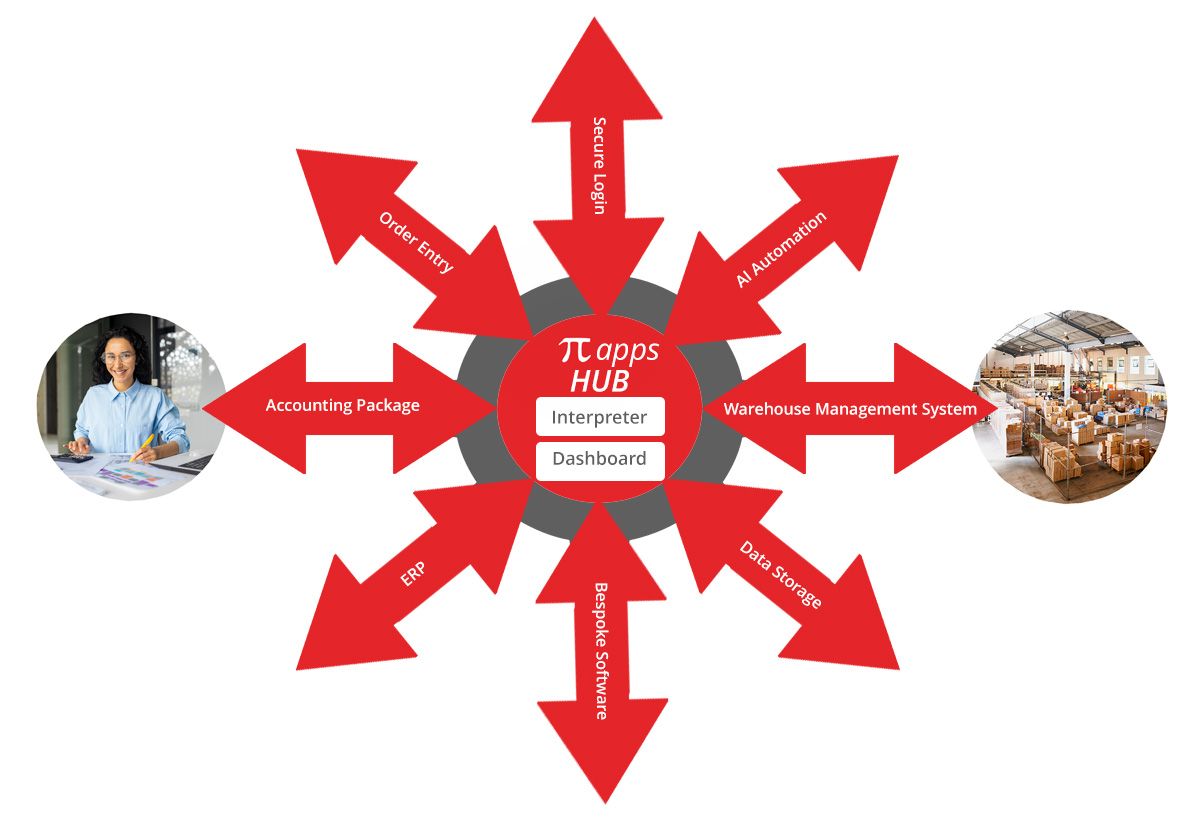
By providing very flexible connectivity, storage and hosting for bespoke software, Piapplications Cloud HUB provides the ideal platform to create a custom enterprise system to meet the needs of your business.
Login and Authorisation:
Cloud hubs can have their own internal login system or can connect to an external auth server. We often create a login system which is a hybrid. Staff are entering via their own corporate staff login and customers have an internal authorisation system. Both of these logins go throught the same login screen.
Storage:
Another element that is very commonly included in hub development is data storage.
Information that's going to be used in the hub or in the third party applications that are connected to the hub may need data storage. Holding the data in the hub is particularly important where access to the data requires a login account.
Another key reason for building data systems in the hub is it makes access to the data by built in software simpler and faster. A typical data storage system for a hub is a Product Information Management system (PIM) which holds all of the technical documentation for a large product set. This information is then available to a front end website, product selection or ordering software, and spare parts management software, all of which need login to access.
An added advantage in building data systems in a hub is that the data is ideally located for use with the AI process called Recovery Augmented Generation (RAG). RAG combines powerful information retrieval with text generation. RAG makes your data search more accurate and relevant.
Piapplications’ Cloud Hub is a powerful and flexible development model that allows us to create unique solutions to your cloud connectivity and automation projects.